Have a question? +336 70 73 89 02
🔞 Not for sale to under 18s
🎃 -40% with code HALLOWEED (on EVERYTHING except vaporizers and gummies) 🎃
Have a question? +336 70 73 89 02
Diabetes or chronic hyperglycemia is characterized by an excess of sugar in the blood, resulting in excessively high glucose levels. It results from a disorder in the assimilation, use and storage of sugars in the diet.
Two essential hormones, insulin and glucagon, enable glucose to be properly assimilated by the body and then released from the liver. When these hormones are balanced, blood glucose levels are stable. In diabetes, however, for a variety of reasons, these hormones fail to function.
- Science distinguishes between several types of diabetes, but in this article we'll focus on type 1 and type 2 diabetes[1].
The first is genetic in origin, affecting young children, and is classified as an autoimmune disease in that the individual's immune system destroys the insulin-producing "beta" cells of the pancreas.
The second, which accounts for around 90% of diabetes cases, generally appears around the age of 40, its causes are not clearly defined (they may be genetic, linked to the environment or to the patient's lifestyle and diet), and it is characterized by insufficient or inefficient insulin production.
The symptoms of the two types of diabetes differ: type 1 diabetes is often marked by weight loss, mood changes and/or blurred vision, while type 2 diabetes is often marked by trembling hands and/or numbness in the limbs[2].
In both cases, diabetes requires treatment and monitoring, usually in the form of insulin injections. If left untreated, diabetes can lead to blindness, kidney failure, heart attack, stroke, lower-limb amputation and nerve damage, among other things.
The number of cases of diabetes worldwide is constantly rising, and is currently estimated at over 400 million[3].
According to several laboratory studies, mainly in 2015 and 2016, CBD has the following effects[4]:
An anti-inflammatory role on disease-induced arterial inflammation;
A neuroprotective effect on nerve inflammation and subsequent pain;
A vasodilatory effect on blood circulation (the hyperglycemia of diabetes weakens vessel walls and promotes blood clotting, stroke)
Antispasmodic action on muscle cramps and gastrointestinal disorders (cramps are common in diabetics).
A calming effect on diabetic agitation syndrome, responsible for insomnia in many patients.
CBD may also delay the onset and progression of type 1 diabetes by preventing the body's own destruction of beta cells, since CBD has autoimmune properties and thus reduces inflammation of the pancreas. CBD oil is also said to regulate oxidative oil in the kidneys, playing a role in renal failure.
On type 2 diabetes, as CBD has an impact on CB1 (one of two neurotransmitters in the brain with links to insulin production), it can be used to treat metabolic disorders caused by diabetes such as obesity.[5]

Finally, one of the first studies carried out on the subject[6] highlighted the reduction and delay in inflammatory cytokine production, thus reducing the incidence of diabetes.
In conclusion, one in four people worldwide has diabetes, and some only discover it at an advanced stage. Although research into CBD is still ongoing, current advances are demonstrating more therapeutic effects than other treatments[7], the latter also having more side effects[8].
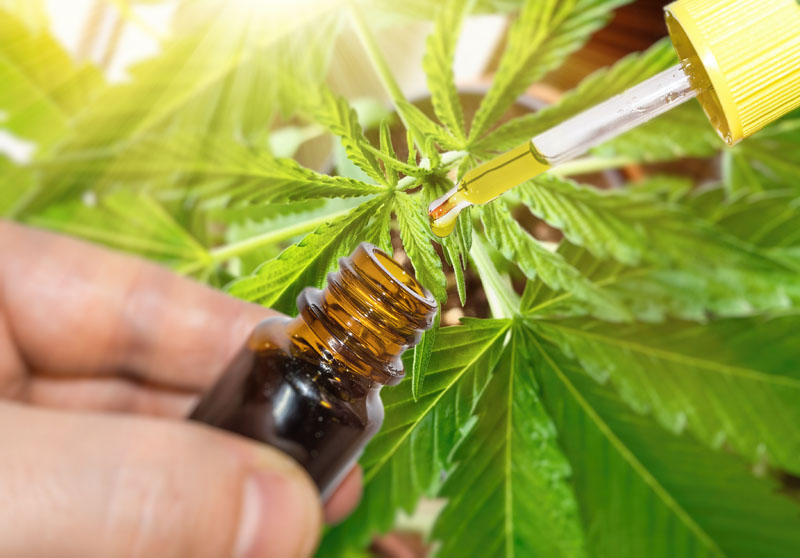

CBD oil is taken in the form of drops placed directly under the tongue using a pipette, allowing it to diffuse more rapidly into the bloodstream for a more immediate effect. In principle, CBD has no side effects. We recommend starting with the lowest dose of CBD.