Have a question? +336 70 73 89 02
🔞 Not for sale to under 18s
🎃 -40% with code HALLOWEED (on EVERYTHING except vaporizers and gummies) 🎃
Have a question? +336 70 73 89 02
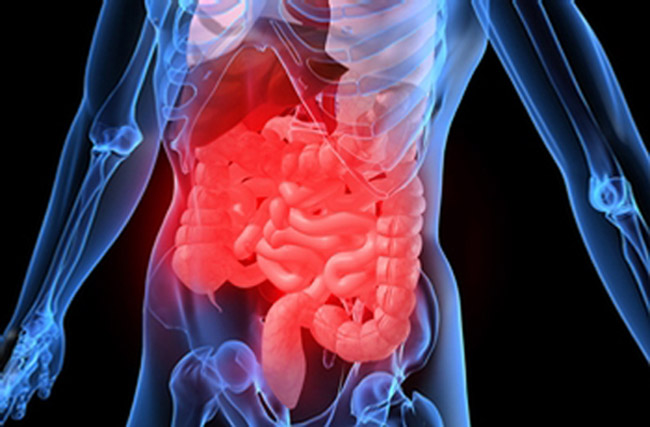
Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). It mainly affects the colon and small intestine, but unlike ulcerative colitis (an autoimmune disease), the inflammation can extend from the mouth to the anus.
Symptoms include severe abdominal pain, diarrhea and, in some cases, non-digestive symptoms (fatigue, malaise, joint inflammation...). They often last several weeks, after which remission phases can extend over several months. When attacks are intense, causing inability to eat and bleeding among other things, the patient will need to be hospitalized.
The causes of the disease, which consists of an inflammation of the walls and deep layers of the digestive tract, can be traced back to several factors:
Studies focusing on the gut's failure to produce an essential fatty acid as a cause of the disease[1], have also opened up new avenues in the search for other possible treatments. Oxidation - the production of cell-damaging free radicals - is also a source of inflammation.
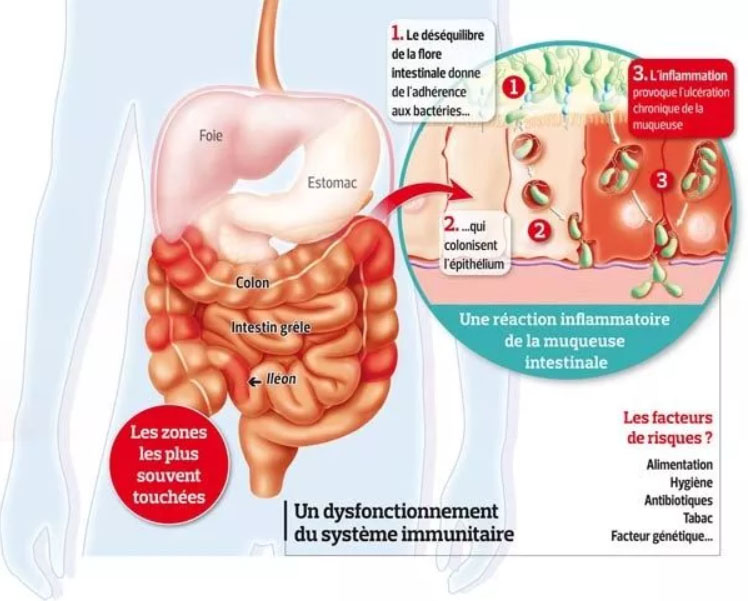
Infographic source: https://sante.lefigaro.fr/sante/maladie/maladie-crohn/quest-ce-que-cest
Conventional treatments involve multidisciplinary management: dietary measures, medication and even surgery (colectomy) in certain cases. To date, Crohn's disease remains incurable, so we can only act on the frequency of attacks and pain management.

CBD or cannabidiol is derived from the hemp plant (cannabis sativa L), but unlike THC, it has no psychoactive effects. This molecule impacts the mammalian endocannabinoid system, i.e. all the neurotransmitters and neuroreceptors present in the nervous system and influencing basic physiological processes (sleep, pain management, inflammation, etc.).
The main receptors are CB1 and CB2, the latter being present throughout the digestive system[2]. Taking CBD will activate these receptors, increasing their impact on the regulation of the gut's inflammatory and immune systems.
In addition to stimulating natural receptors, numerous studies have highlighted the following characteristics of the CBD molecule:
More generally, another randomized clinical study[6] from 2013 involved a group of Crohne's disease patients given CBD+THC* and another group given placebo. After 8 weeks of treatment, of the 11 subjects given CBD, 10 showed significant improvement, and of these 10, 5 went into complete remission.
Finally, a 2012 Italian study[7] on cannabidiol and inflammatory bowel disease concludes: "The beneficial effects of CBD have been widely demonstrated in chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). This molecule possesses an extraordinary range of beneficial effects that can slow the course of the disease, improve symptoms and potentially increase the efficacy of drugs actuallyavailable for the treatment of disabling intestinal disorders such as ulcerative colitis and also Crohn's disease. Because of its low toxicity even in humans and its complete absence of any psychotropic side effects, CBD may represent a new molecule or one of the lead compounds for developing new pharmacological approaches to improve the treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases."
* THC is a prohibited substance in France (if levels exceed 0.3%).
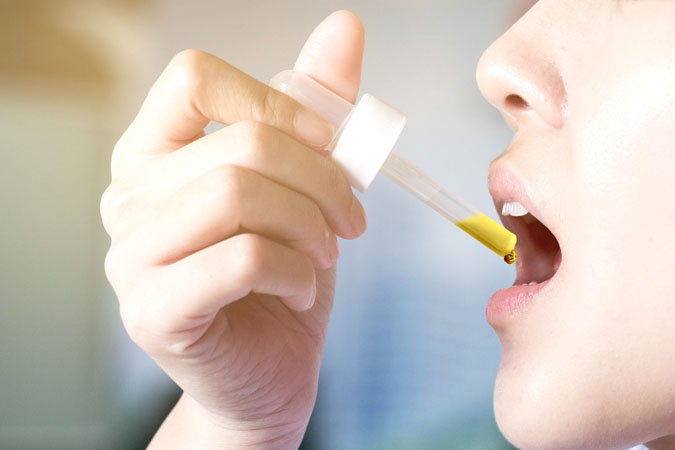

Taking cannabidiol in oil form is one of the most effective ways to consume it. All you need to do is place a few drops directly under the tongue, using a pipette, for about a minute.
This allows CBD to enter the bloodstream very quickly, and ultimately the endocannabinoid system. Although taking CBD has no side effects, as each individual reacts differently to the molecule, it is advisable to start with the lowest dosage and then increase the number of drops until relief is achieved.
Before taking any CBD, you should seek the advice of your doctor.



