Have a question? +336 70 73 89 02
🔞 Not for sale to under 18s
🎃 -40% with code HALLOWEED (on EVERYTHING except vaporizers and gummies) 🎃
Have a question? +336 70 73 89 02

Have you ever heard of THCa? If you have, it's probably because you'd like to know more about it.
What is THC-a, how is it synthesized, what is its role, its legal status, what are its effects and its specific features? Without further ado, here are the answers to your questions!
Although it may sound like THC-P, THCV and THCJD, THC-a is not quite one of these cannabinoids. It's actually a cannabinoid acid, known as tetrahydrocannabinolic acid.
Like most chemical compounds in hemp and cannabis, THCa is synthesized by CBGA or cannabigerolic acid, often referred to as the parent cannabinoid. As the plant grows, some of the CBGA contained in the plant is converted into CBGa and THCa by enzymes produced by the glandular trichomes.
THCa's role is to keep cannabis plants healthy. When the plant reaches maturity, THC cracks the protective membrane of dead, dying or damaged cells. As a result, old cells can be replaced by new ones.
In humans, this is exactly what the process of Programmed Cell Death describes. This process is extremely important, as it is when this process fails that diseased cells remain active, proliferate and can lead to cancer.
At the molecular level, the structure of THCa is quite similar to that of THC, with one difference: THCa has two carboxyl groups. In chemistry, it is therefore known as 2-COOH-THC.
These carboxyl groups make the difference between a cannabinoid acid and a cannabinoid. They are highly sensitive to heat and light. That's why cannabinoid acids are only found naturally in fresh, undried plants. During drying, light and heat destroy these carboxyl groups in a process called decarboxylation. So, if you've followed the reasoning, THC is created by the decarboxylation of 2-COOH-THC (THCa).
During this stage, around 70% of THCa is converted into THC, the rest being destroyed by heat. And if this process is maintained for longer, THC itself degrades. The 4 hydrogen groups contained in Tetrahydrocannabinol are also destroyed, leaving Cannabinol (CBN).
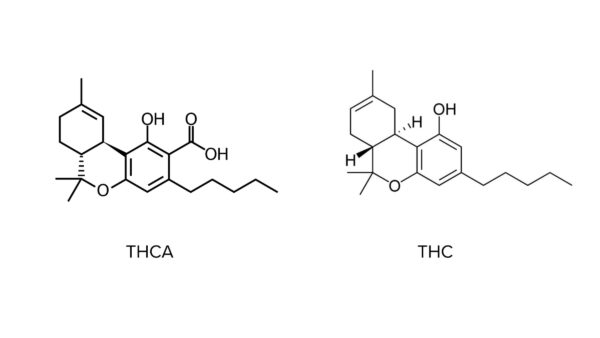
As you can see, THCa fears heat and light, and changes to THC when exposed to them. To experience the effects of THCa, it's essential to eat fresh, not dried, cannabis, because if it were smoked, it would automatically be converted during combustion.
According to the limited preliminary research available today, THCa is non-psychoactive. Researchers have estimated that it has only a very slight impact on CB1 and CB2 receptors (around 60 times less than THC). However, this doesn't mean that it has no effect at all, because despite its low interaction, it is capable of acting on certain mechanisms managed by the endocannabinoid system, such as: COX-1 release, COX-2 inhibition, TNF-Alpha inhibition, interleukin-10 release. This means it could have a positive influence on :
Other preliminary research has also revealed an antiemetic action, i.e. a capacity to combat nausea and vomiting, which could make it a valuable molecule in a variety of cases (against car sickness, the side effects of cancer treatments, etc.).
Like many other cannabinoids and cannabinoid acids, THCa's legal status has been in a state of flux recently. It was included in the list of "new cannabinoids" classified as narcotics announced on 22/05/22 "This list notably includes H4-CBD, H2-CBD and certain synthetic cannabinoids with a chemical core called benzo[c]chromene, such as HHCPO, THCP and THCA."
But this decision was amended a week later, so that THCa would be excluded from the classification "as long as their THC content complies with the 0.3% threshold laid down in the Order of December 30, 2021 implementing article R.5132-86 of the Public Health Code".
At European level, there are no regulations specifically targeting THCA, so regulation varies from state to state.
In most EU member states, THCa is regulated in the same way as THC, with the exception of Spain, which is more permissive and therefore does not regulate it.
This means that, in general, THCA is legal as long as its level does not exceed that authorized for THC.
The sale of products containing THCa in France is therefore legal as long as the finished product contains less than 0.3% THC.
In theory, this means that if you find edible products or concentrates such as candies, oils and other THCa crystals, they will be totally legal.
However, things are less clear-cut when it comes to flowers or resins, because as we've seen, THCa degrades into THC under the action of heat and light.
THCA is an interesting cannabinoid acid which has attracted the attention of researchers both for its role in mature cannabis plants and for its decarboxylation mechanism.
Although it came very close to being banned, it remains legal, and some stores are already selling it in various forms. Nevertheless, it may not be long before the ANSM takes another look at THCA's classification, in view of its possible degradation into THC.