Have a question? +336 70 73 89 02
🔞 Not for sale to under 18s
🎃 -40% with code HALLOWEED (on EVERYTHING except vaporizers and gummies) 🎃
Have a question? +336 70 73 89 02
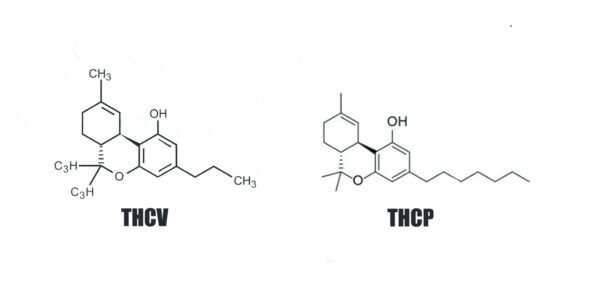
In addition to H4CBD, two other molecules will be available on the French and European markets in 2023: THCV and THCP. These are two of the many cannabinoids present in cannabis. As you probably know, alongside the two best-known and most concentrated compounds, THC and CBD, there are over 130 cannabinoids present in cannabis.
As their names suggest, tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV) and tetrahydrocannabiphorol (THCP) are closely related to THC, but their effects are different, and in some cases even opposite. Follow us as we explain it all!
THCV was discovered in the 1970s. The molecule was mainly exploited for legal purposes. After its presence was found to be higher in certain African varieties, it was used to determine the origin of cannabis confiscated by police and customs authorities in various countries.
The discovery of THCP (and CBDP for that matter) is more recent. It was only discovered in 2019. It was made by a team of Italian researchers led by Professor Giuseppe Cannazza of the University of Modena.
Today, these two molecules are attracting renewed interest. Not only on the part of consumers, curious or looking for stronger effects than CBD, but also on the medical side, where there is interest in the many applications in which these substances could make a real difference.
These two compounds, naturally present in the plant, have been little noticed and little studied due to their low concentration. By comparison, THC concentrations regularly exceed 20%, while THCV rarely exceeds 4% and THCP is generally around 0.20%. Certain chemical manipulations are therefore necessary to increase these levels and ensure that they reveal their effects when consumed. Products marketed for their high THCV and THCP content are therefore classified as semi-synthetic.

Like THC, THCP and THCV bind to CB1 receptors, but they also interact with CB2 receptors, giving rise to the effects of CBD. Interestingly, in its natural state, THCV, itself not very psychoactive , multiplies the psychoactive effects of THC. And THCP is considered to be 30 times stronger than THC .
But we'll have to wait a little longer to find out more, as their use and research are still in their infancy, so data on their actual effects is still scarce.
Although the molecular structures of THC, THCV and TCHP are quite similar, their effects all seem to differ.
THCV is considered a "neutral" cannabinoid: it does not provide the psychoactive effects of THC. But this is not the case, as its effects vary according to concentration. When THCV concentration exceeds 10%, it is said to activate CB1 and CB2 receptors, triggering intense relaxation and mild euphoria . Other effects include the following:
Studies1 have also revealed that this substance may possess neuroprotective qualities. The substance could therefore be used to combat certain neurodegenerative diseases (such as Alzheimer's or Parkinson's), as well as obesity and type 2 diabetes, like CBD.
According to studies, THCP seems to bind powerfully to endoreceptors . Its effects on them are rapid, powerful and long-lasting. Although still relatively unknown, tests2 have shown that the substance can reduce sensations of pain and nausea, as well as inflammation. Antioxidant and anti-epileptic properties have also been demonstrated.
It is also a product with powerful psychoactive effects, which can trigger the effects desired by consumers (euphoria, self-consciousness, increased appetite...), but also more harmful ones such as paranoia, stress, tachycardia... and of course, dry mouth!
As far as legality is concerned, both substances have benefited from a legal loon which has enabled them to remain legal for some time. Nevertheless, in view of their initial results among consumers and in the laboratory, we thought that THCV might remain available longer than THCP because of their psychoactivity. And we were right: as of June 3, THCP is illegal in France .
Notes :