Have a question? +336 70 73 89 02
🔞 Not for sale to under 18s
🎃 -40% with code HALLOWEED (on EVERYTHING except vaporizers and gummies) 🎃
Have a question? +336 70 73 89 02
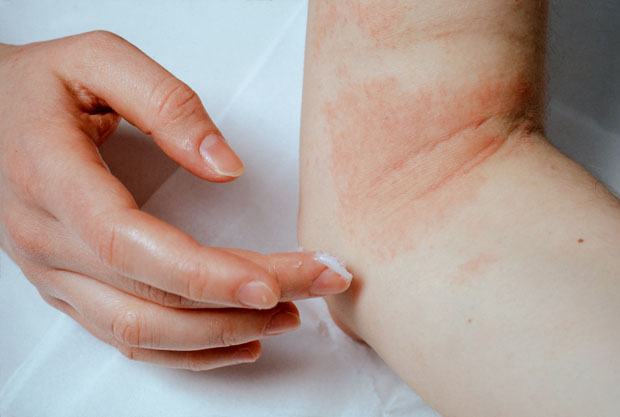
Eczema is a chronic inflammatory skin disease. It is not contagious. Depending on the cause, eczema can take several forms:
Depending on the symptoms, there are various types:
Traditional treatments involve either identifying the allergen and isolating/desensitizing it, or using local antiseptics or dermocorticoids, or antibiotics, not without side-effects if applied for prolonged periods.
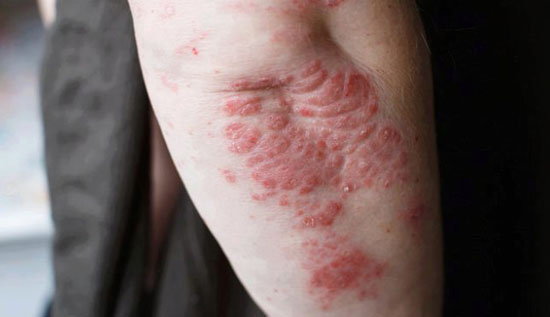
Psoriasis is also an inflammatory skin diseasecharacterized by erythematosquamous lesions. It affects between 2% and 4% of the world's population. Auto-immune, this disease results from an abnormal reaction by the immune system, which wrongly identifies a substance as an invader. The reaction does not stop, and new skin cells are created and pushed to the surface at a rate that does not allow dead cells to be eliminated. This accumulation of skin forms psoriasis. The white scales are composed of dead skin cells, and the redness comes from an influx of blood.
Psoriasis also takes many forms: plaques on the body, scalp, nails, or psoriasis of the folds or mucous membranes... It is never contagious, but particularly affects patients' quality of life, especially in its most severe forms[1].
As with eczema, treatments are often local and long-lasting, combining dermocorticoids and vitamin D3.

CBD is a molecule derived from the hemp plant, like THC, with the difference that it has no psychotropic properties. Under study for years by scientific researchers around the world, CBD has the unique ability to stimulate the body's natural endocannabinoid system (ECS). Taken in oil form under the tongue or applied directly to the skin, it penetrates the bloodstream and impacts the receptors making up our SEC, notably CB1 and CB2. This system, also widely studied, is responsible for the proper functioning of several basic functions such as sleep, mood, appetite, pain, and in particular: inflammation and immune system function[2].
* It is important to consult your doctor before taking CBD. CBD is not a substitute for your usual treatment.
An initial study dating back to 2007[3] showed encouraging results. It shows that cannabinoids, including CBD, slow the growth and division of skin cells involved in psoriatic skin eruptions.
In the case of psoriasis, which is an autoimmune disease, inflammation is caused by a poor immune system response, and CBD's immunomodulatory properties reduce inflammation. Hence the response of cannabidiol in the treatment of psoriasis, as demonstrated by a 2017 study conducted by the University of Colorado[4].
Psoriasis is often accompanied by additional, non-cutaneous symptoms such as arthritis. As explained in this previous article, CBD could also relieve this rheumatism.
Also in the University of Colorado study, Dr. Robert Dellavalle states that " one of the most promising functions of cannabinoids is in the treatment of itching ".
The endocannabinoid system naturally produces a neurotransmitter, anandamide (fatty acid family). CBD will activate this process and raise anandamide levels, resulting in an anti-inflammatory effect. As with acne and other skin conditions, inflammation is often the cause of skin symptoms, and CBD regulates the immune response to reduce inflammation.
By the same token, CBD also acts to reduce stress and thus the development or accentuation of these skin diseases.
Psoriasis and eczema rarely leave scars, especially when properly treated. However, excessive scratching can thicken the skin and, in some cases, lead to scarring[5].
An Italian clinical study published in 2019[6], carried out on a small sample, administered cannabidiol directly to the skin twice a day to 20 patients with psoriasis-related scars and atopic eczema.
After three months of treatment, the researchers found that CBD had significantly improved the appearance of the skin, particularly its elasticity and hydration..
A recent Hungarian study (2019)[7] states that "clinical studies over the past 20 years have unambiguously confirmed that cannabinoids, including CBD, are deeply involved in the maintenance of skin homeostasis (stabilization), barrier formation and regeneration. Its disruption is implicated in several widespread diseases such as eczema and psoriasis.
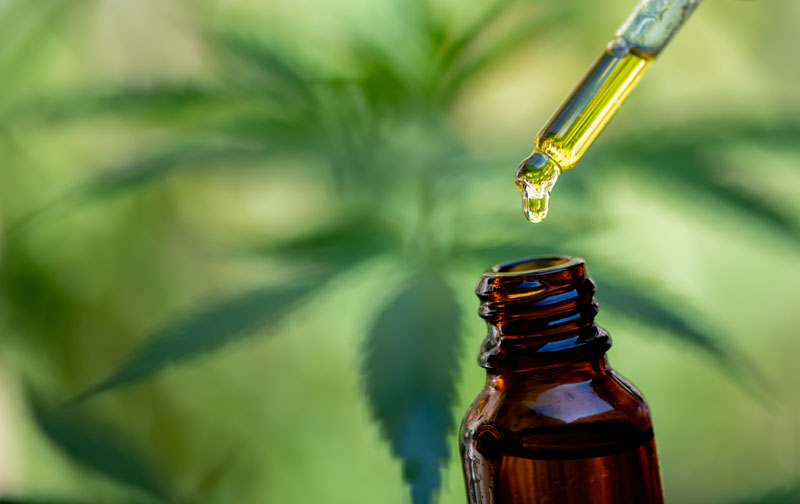

Taking cannabidiol in oil form is one way to consume it. Simply place a few drops directly under the tongue for about a minute. Although cannabidiol has no known side effects, it's advisable to start with the lowest dose and gradually increase the number of drops until you feel relief.
For post-psoriasis and post-eczema scars, we recommend using CBD in ointment or cream form, or applying CBD oil (5% concentration) directly to the skin.
Before taking any CBD, you should seek the advice of your doctor.